Enterprise Audit Execution Workflow
Solving Fundamental Coordination Failures in Legacy Audit Platforms
The problem
Users from two legacy audit platforms were abandoning enterprise software for Excel spreadsheets due to fundamental workflow coordination failures. External tracking systems had become necessary because the software couldn't coordinate basic audit handoffs between auditors and reviewers.
Timeline:
3 months
My role:
Lead UX/UI Designer
Team:
User researcher, project manager, technical product owner and the development team
Discovery Process
My initial brief was to create a streamlined audit workflow that would reduce excessive clicking and navigation time. With no analytics available, I conducted competitive benchmarking of both legacy platforms to understand the differing user mental models that would need accommodation in a unified solution.
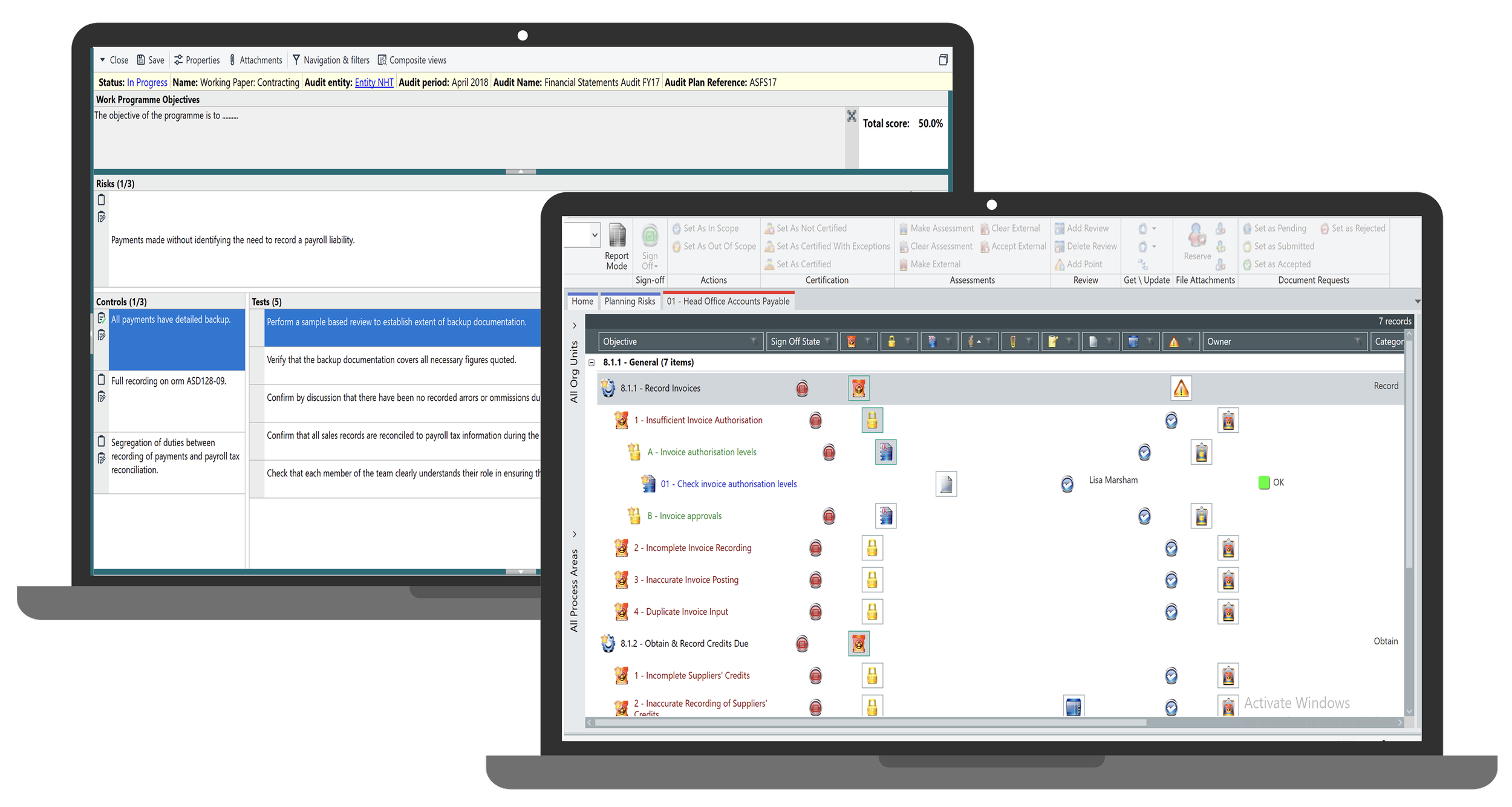
Platform A Issues:
Hierarchical navigation requiring clicks through each level (objective → risk → control → test)
Unlabeled ribbon interface with many disabled features
Assessment required at every hierarchy level
Audit status tracking separated across different tabs
Platform B Issues:
Quadrant layout with space constraints and poor feature discoverability
Simplified workflow but separate checklist system requiring navigation to another area
No clear workflow progression
Critical Discovery
During pre-testing interviews, users revealed the actual scope of the coordination problem. One user explained: "We actually have a spreadsheet outside of the legacy software that we use for tracking each step. The auditor documents when they complete tasks, then contacts the reviewer to let them know it's ready for review. We also use it to document our review, so we know when it's complete."
This revelation exposed additional coordination failures throughout the audit process:
"We're not getting notifications when items are put for review"
"If a review isn't assigned to a specific person it gets lost and can't be traced"
"The elements of our brief are split across several screens"
"It's very clicky - lots of boxes to click into and open up just to do data entry"
Key Insight: Users weren't simply frustrated with interface efficiency; they were maintaining comprehensive shadow systems because the enterprise software fundamentally failed to coordinate essential workflow handoffs between team members.
Solution Strategy
I developed a design strategy focused on creating consolidated audit management that would eliminate external tracking needs while accommodating both platform user groups. The solution required careful balance between unified functionality and respect for existing user mental models.
Core Solutions:
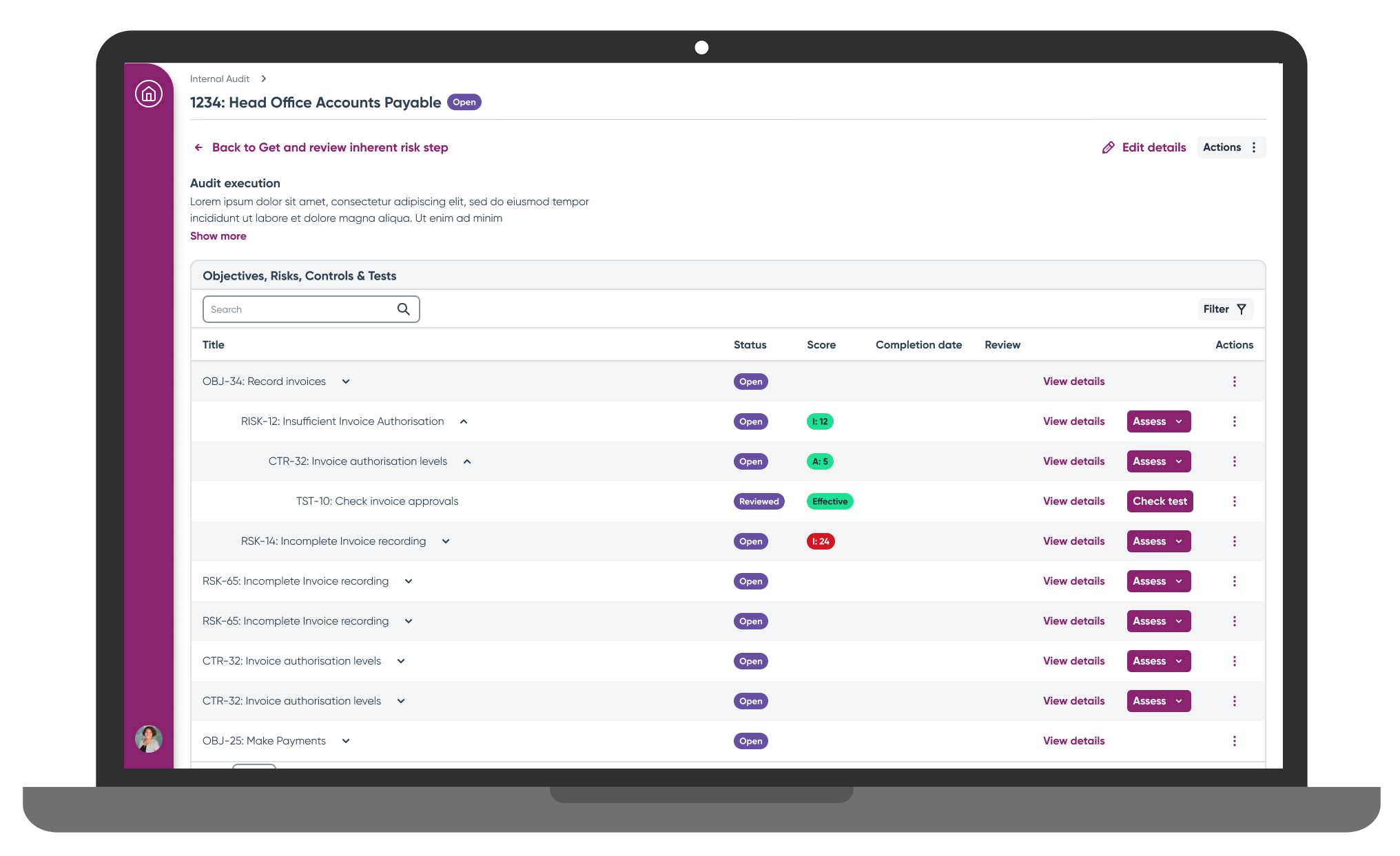
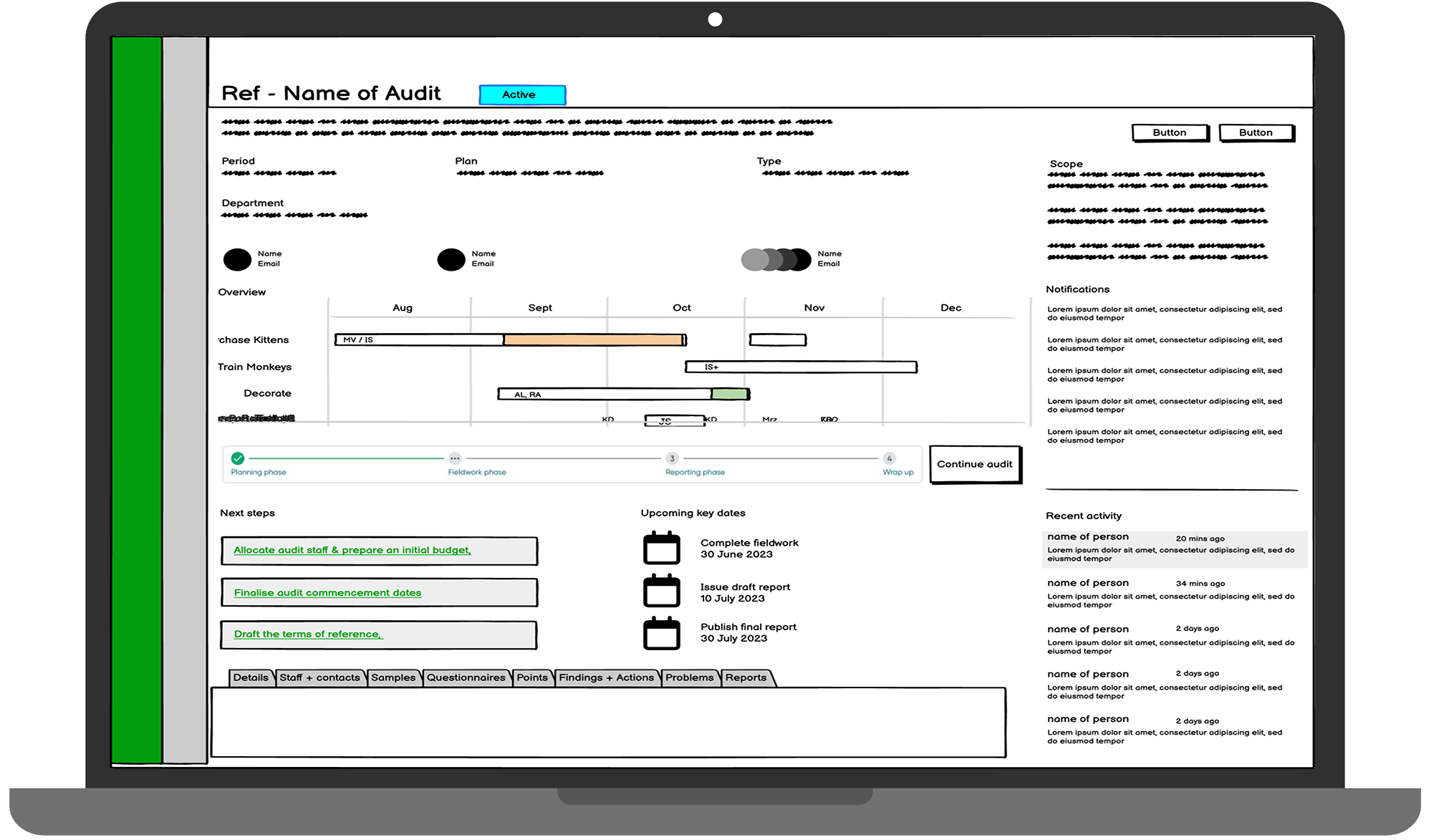
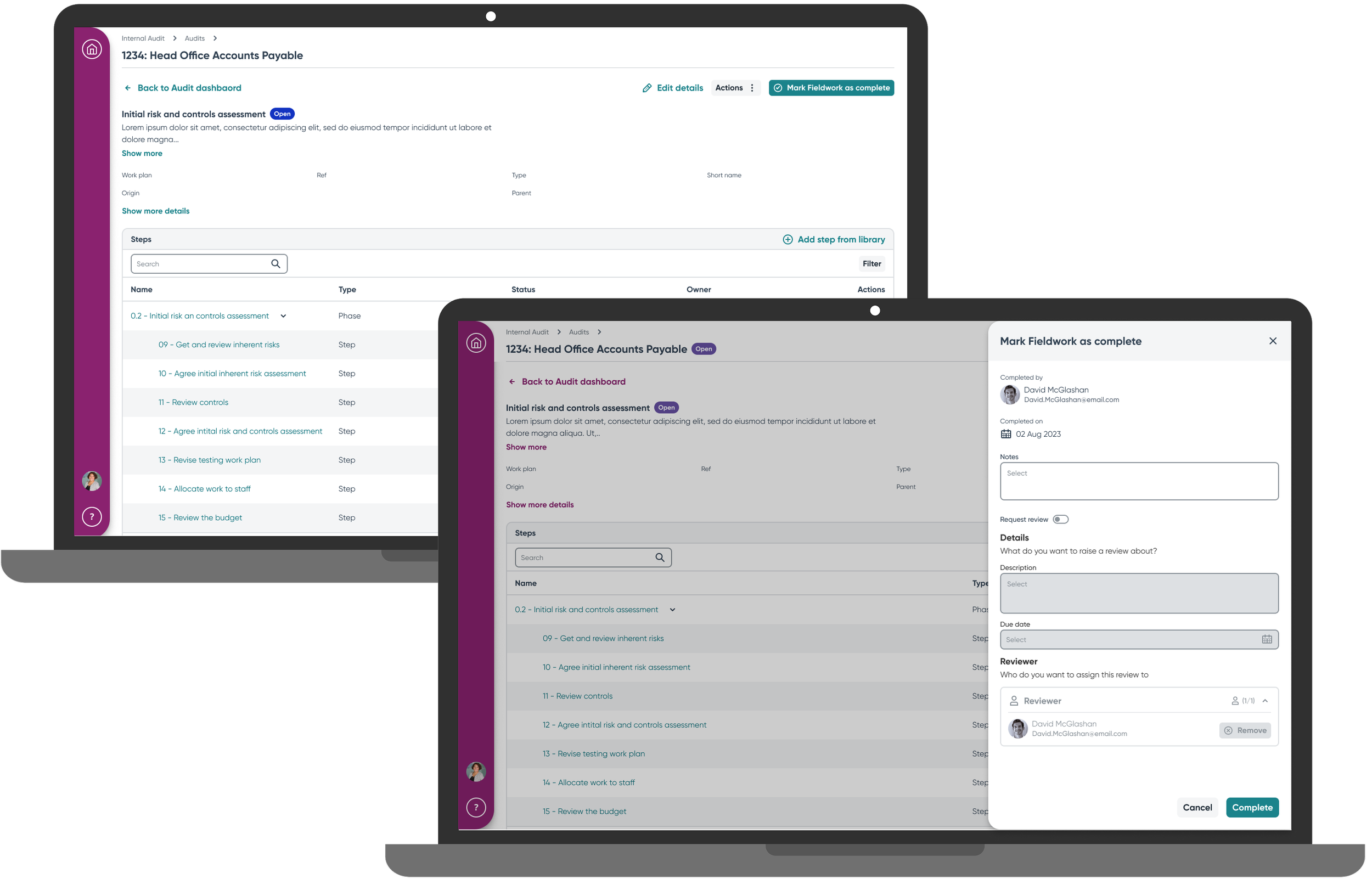
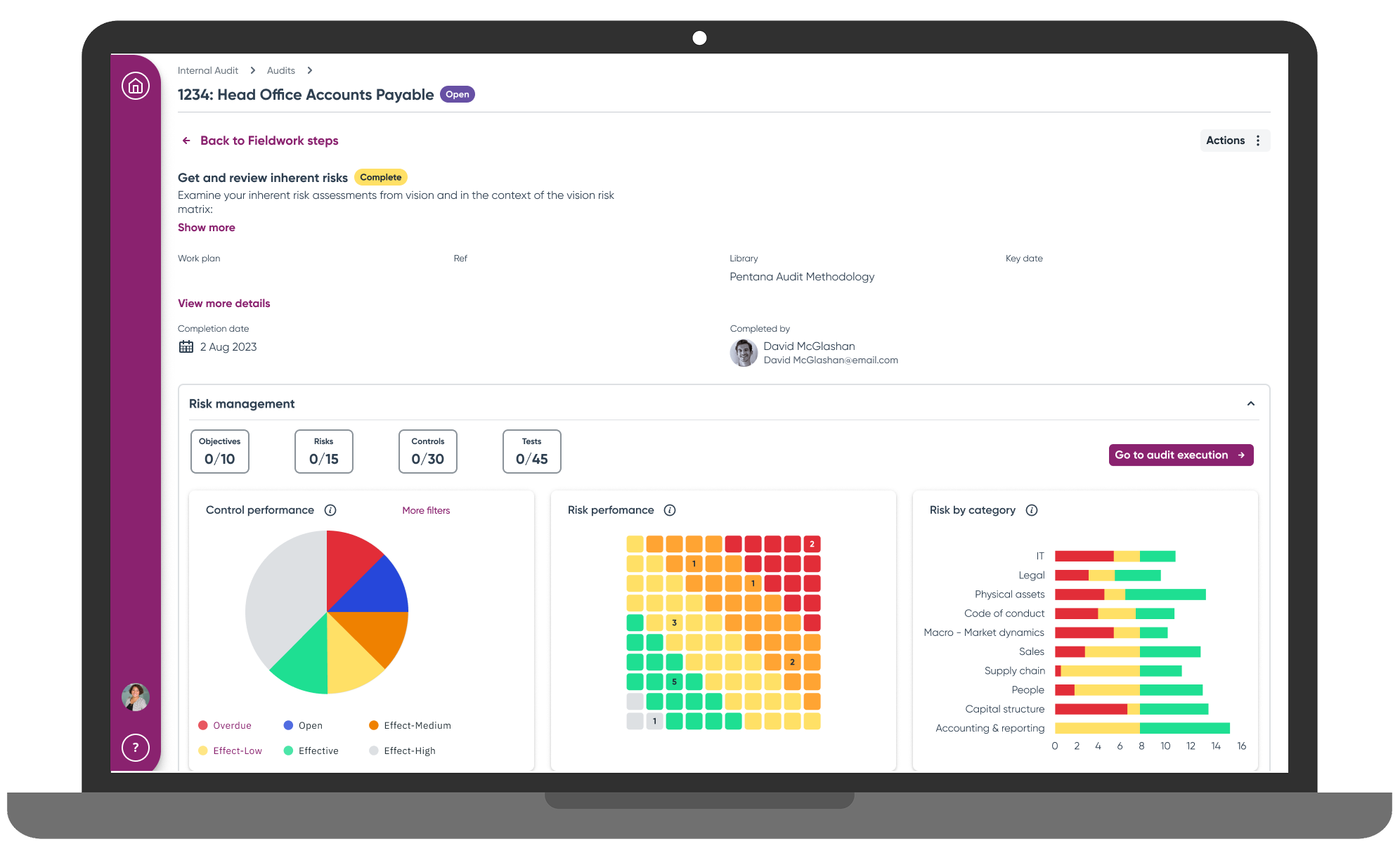
Audit Hub Dashboard became the central coordination point, providing real-time progress visibility across concurrent audits. Rather than scattering information across multiple screens, the hub consolidated critical details into a single view with quick navigation links that reduced screen transitions significantly.
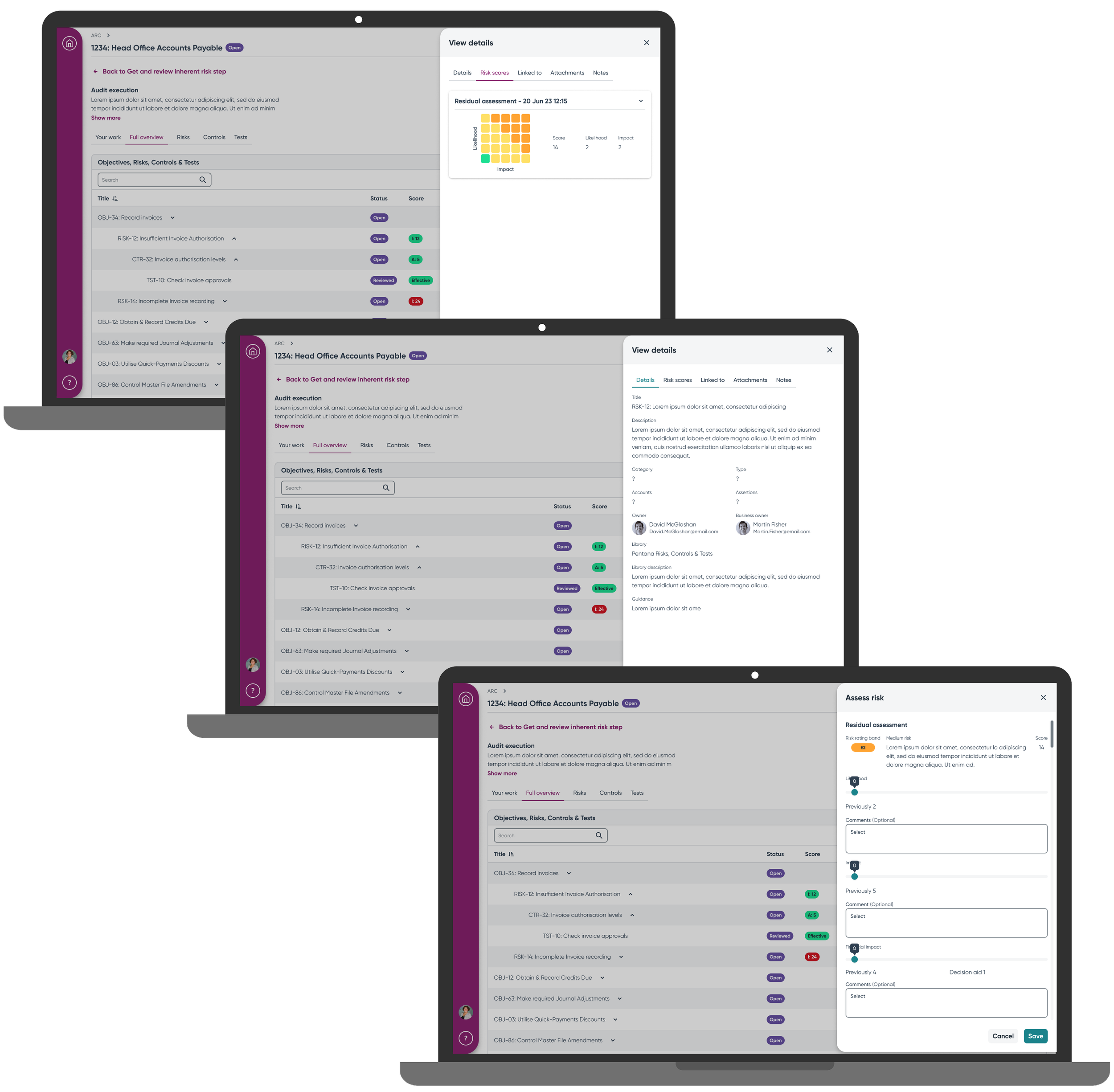
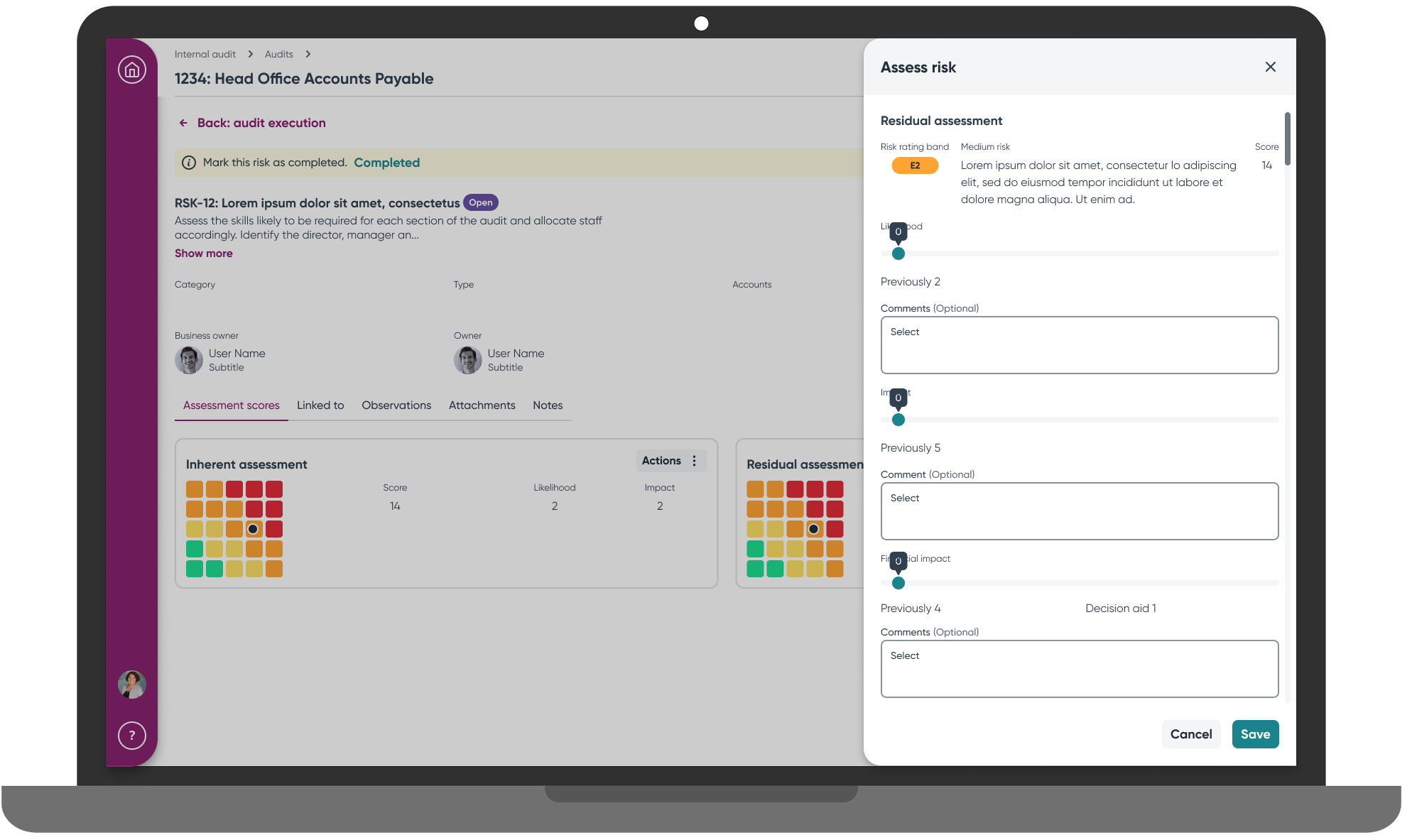
Flexible Assessment Options accommodated the different approaches users had developed on legacy platforms. A hierarchical table showed objective-risk-control-test relationships clearly, while a quick assess feature via slide-in drawer served efficient users who needed rapid completion paths. Detailed record views remained available for thorough assessment when needed, and progressive disclosure replaced the overwhelming feature ribbons that had confused users on legacy platforms.
Validation Results
Round 1 Testing Feedback:
"It's much less clicky, and that's one of our big complaints about the current system. It flows in a way where you can see what comes next"
"This shows a lot visually on one page, which right now is scattered around different parts of the legacy software"
However, testing revealed specific issues requiring iteration. Users didn't understand "Sign off" terminology, the audit execution page felt cramped, and critically, there was no review process to address the coordination failures users had described.
Round 2 Testing Improvements:
I designed an embedded review workflow that addressed the core coordination failure by building review handoffs directly into task completion actions. The system included an optional review step to accommodate users whose processes didn't require review functionality, while clear status indicators and notification systems ensured proper handoff communication between auditors and reviewers.
Additional improvements included:
Changed "Sign off" to "Mark as complete" achieving 100% user comprehension
Hierarchical table clearly showed object relationships
Removed unused fields reducing visual noise
Final validation confirmed that all users understood the revised completion workflow. More importantly, users confirmed that the embedded review system addressed the fundamental coordination problems that had driven them to external spreadsheet solutions.
Outcomes
Design Achievements:
Unified workflow accommodating two different legacy user mental models
Eliminated need for external spreadsheet tracking through embedded coordination
Reduced navigation from multiple screens to consolidated hub view
Flexible assessment options supporting different auditor preferences
User Impact:
Successful task completion without external tracking systems in final testing
Improved workflow comprehension across both user groups
Reduced coordination failures through embedded review handoffs
Business Enablement:
Delivered unified audit execution capability for enterprise sales
Created foundation for competitive advantage in risk management market
Key Learnings
The most critical process insight emerged from recognizing that user interviews revealed the assignment addressed symptoms rather than root causes. The initial brief focused on interface clicks while the real problem involved coordination failure. Discovery-driven research enabled a solution pivot from interface optimization to workflow coordination that delivered substantially greater user value.
The research process reinforced the importance of understanding actual work patterns rather than just system functionality. User workarounds consistently reveal fundamental product gaps that requirements documents often miss entirely.
What I'd Change: Include workflow shadowing sessions to observe audit processes in their natural context, ensuring solutions align with real coordination needs rather than assumed workflows based on system capabilities alone.
Next Steps
Future development should expand module features to achieve parity with legacy platform capabilities while building on the coordination foundation established in this project. Key opportunities include implementing audit assistance based on historical data patterns, monitoring elimination of external tracking systems post-launch, and measuring workflow coordination efficiency improvements through establishing analytics infrastructure.
Note: Impact measurement is limited by lack of analytics infrastructure on the platform. Quantifying time savings, completion rates, and feature utilisation will require establishing measurement capabilities currently unavailable.